What is Aerial Annotation?
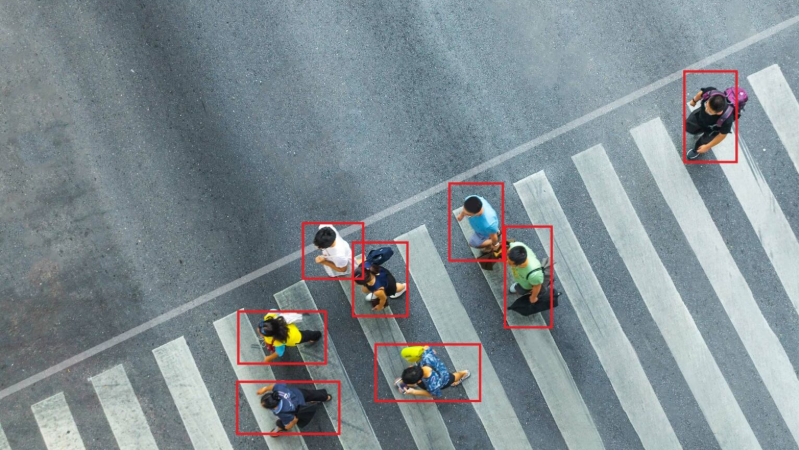
Aerial Annotation is the process of labeling and tagging data captured from aerial sources such as drones, satellites, or aircraft to make it usable for AI and machine learning models. It involves identifying and marking objects like vehicles, buildings, roads, crops, and water bodies, as well as segmenting land areas and detecting patterns. This annotation is crucial for applications in precision agriculture, urban planning, disaster management, environmental monitoring, and autonomous navigation, enabling accurate analysis, predictive modeling, and data-driven decision-making from aerial imagery.
Why is Aerial Annotation Important?
AI models rely on accurately labeled aerial data to:
- Detect and classify objects like vehicles, buildings, and trees.
- Map roads, rivers, and other linear or irregular features.
- Monitor environmental changes and urban development.
- Support disaster management and emergency response planning.
High-quality aerial annotations ensure better model accuracy and reliability, especially in applications where spatial precision is critical, such as autonomous drones, smart city planning, agriculture monitoring, and defense surveillance.
Types of Aerial Annotation

Image and Video Annotation
Bounding boxes highlight objects like vehicles, rooftops, or ships. Polygon annotation captures irregularly shaped areas such as farmland, lakes, or forests. Semantic segmentation labels every pixel to classify terrain, roads, and vegetation. Keypoint annotation marks landmarks for mapping or navigation, while polylines track linear features like roads, railways, and rivers. Frame-by-frame video annotation enables object tracking for surveillance, traffic monitoring, and wildlife studies.
Multisensor and 3D Annotation
LiDAR and RADAR data can be annotated to generate 3D point clouds, helping AI models understand elevation, terrain, and spatial relationships. These annotations are vital for autonomous aerial vehicles, topographical mapping, and urban planning.


