How Polygon Annotation Works
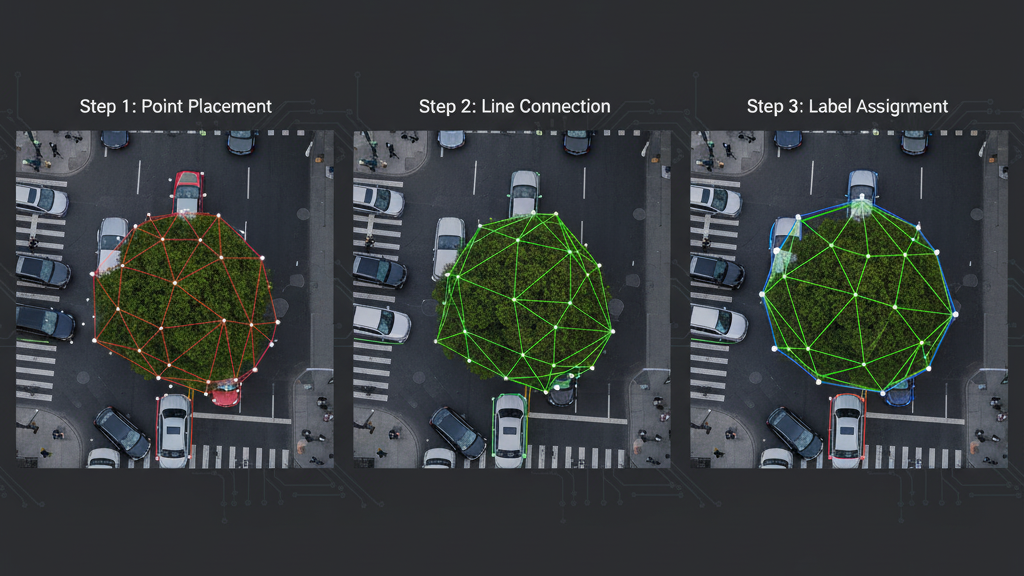
Vertex Placement: Annotators click along the edges of the object to place points.
Line Connection: Each point is connected to form straight lines, ultimately closing the shape.
Class Labeling: The polygon is assigned a class label (e.g., “car,” “tree,” “tumor”).
Verification: The shape is checked to ensure it accurately covers the object without missing edges or including background.
Applications of Polygon Annotation
- Autonomous Vehicles: Labeling irregularly shaped vehicles, traffic signs, pedestrians, and obstacles.
- Medical Imaging: Outlining tumors, organs, or lesions for AI diagnostic models.
- Satellite & Aerial Imagery: Mapping land parcels, buildings, forests, rivers, and roads.
- Retail & Fashion: Annotating products in images for visual search and inventory management.
- Robotics & AR/VR: Detecting and segmenting objects with complex shapes for manipulation or immersive experiences.


