What is a Multisensor System?
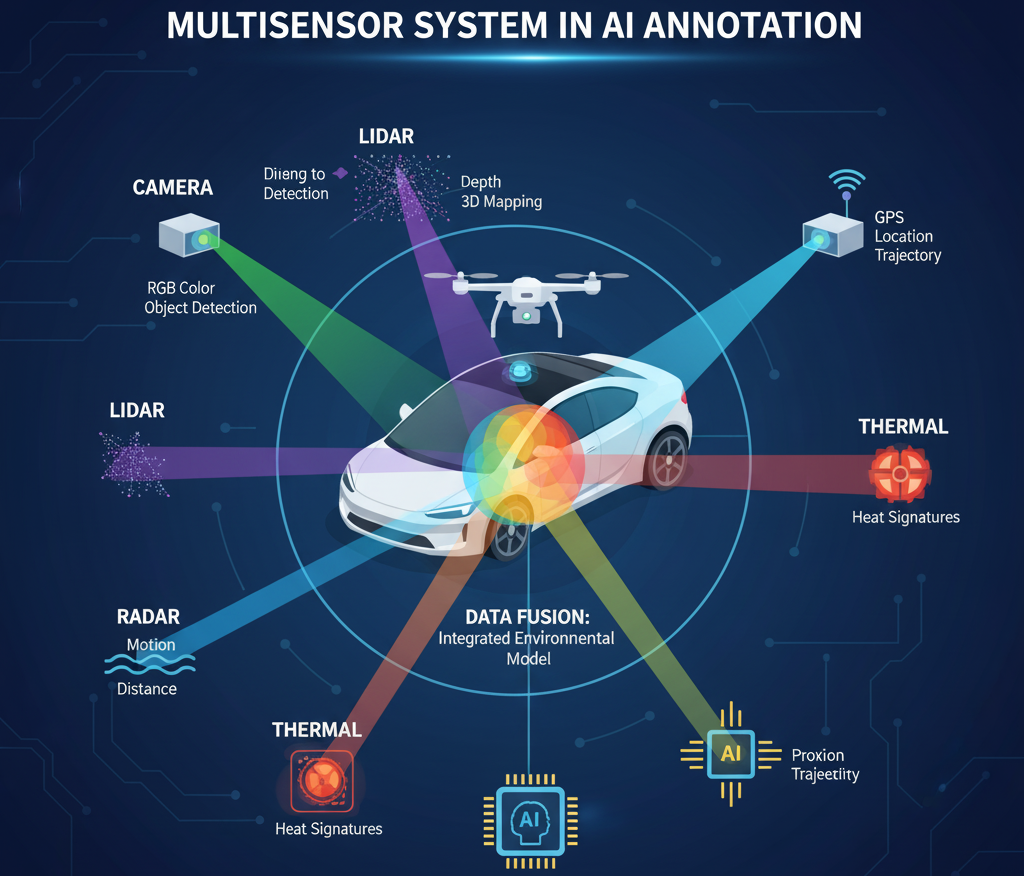
A multisensor system combines data from different sensor types, such as:
- RGB Cameras – capture color images (visual context).
- LiDAR (Light Detection and Ranging) – provides 3D point clouds for depth and distance.
- Infrared/Thermal Cameras – capture heat signatures, useful for night or low-visibility conditions.
- Radar – measures distance and velocity, especially in adverse weather.
- Ultrasonic Sensors – detect close-range objects.
- GPS/IMU Sensors – provide positional and movement data for georeferencing.
By fusing these sensor inputs, a multisensor system can create a comprehensive representation of the environment.
Applications
- Autonomous Vehicles: Annotating road scenes using LiDAR, camera, radar, and GPS to detect cars, pedestrians, lanes, and obstacles.
- Surveillance & Security: Fusing thermal, RGB, and infrared to annotate people or suspicious activities in different lighting.
- Agriculture: Combining RGB, multispectral, and LiDAR sensors to annotate crop health, terrain, and irrigation systems.
- Robotics: Annotating 3D maps of indoor/outdoor environments for navigation and obstacle avoidance.

