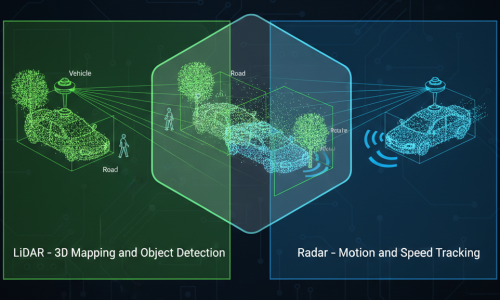
How LiDAR Is Used in Annotation
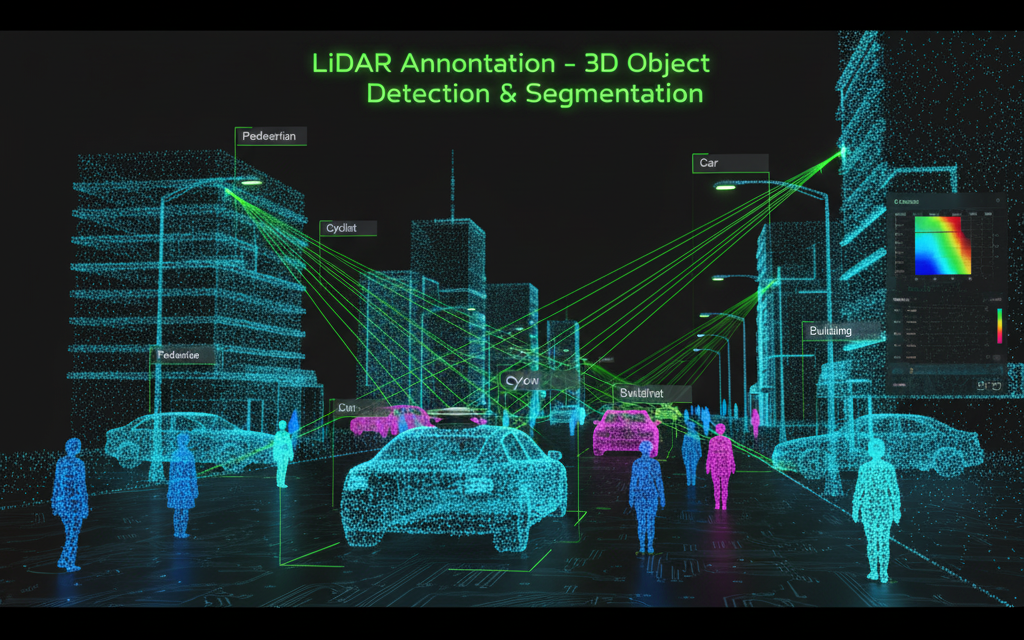
In AI datasets, LiDAR data is annotated to help models understand the 3D world. Typical annotation tasks include:
- 3D Bounding Boxes – Drawing boxes around vehicles, pedestrians, trees, or other objects in 3D space.
- Segmentation – Labeling each LiDAR point according to object type (e.g., road, car, building).
- Sensor Fusion Annotation – Merging LiDAR data with camera images for more accurate labeling.
- Depth & Distance Mapping – Annotating the relative distance of each object from the sensor.
How Radar Is Used in Annotation
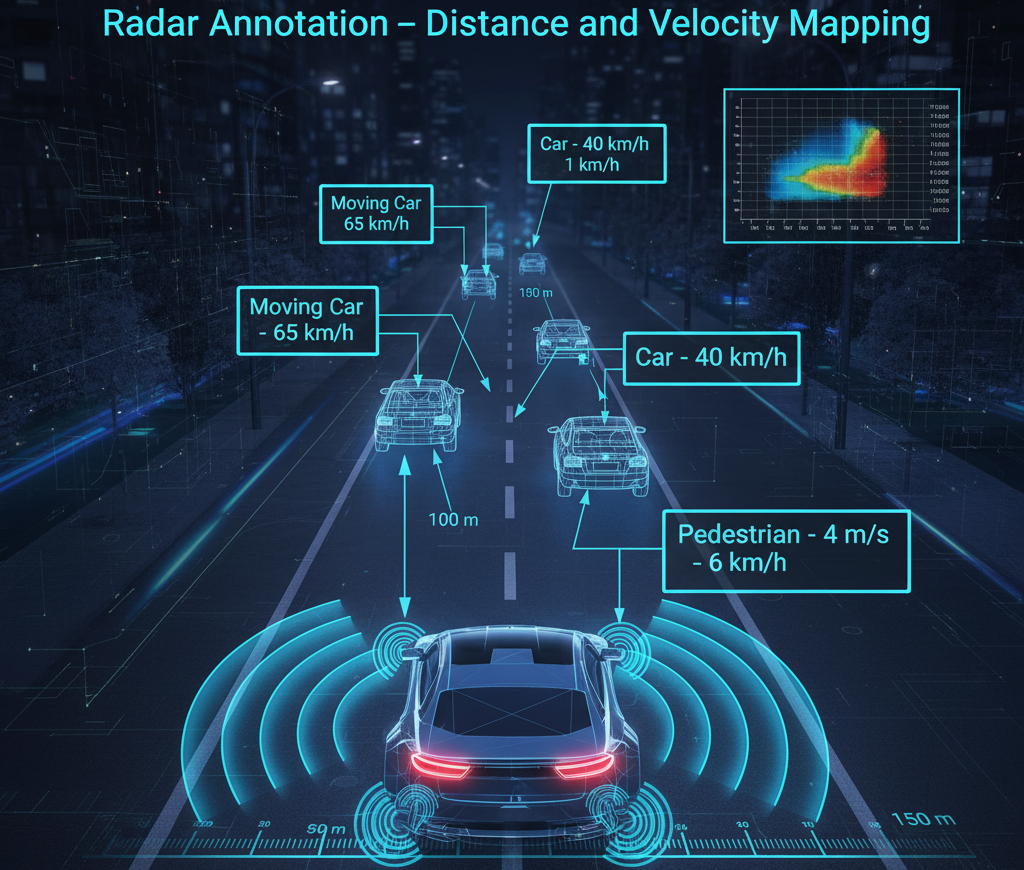
Radar data annotation involves identifying and labeling objects based on radar reflections and motion patterns:
- Object Detection & Tracking – Annotating moving or stationary targets (vehicles, people, obstacles).
- Velocity Annotation – Labeling speed or direction of moving objects.
- Sensor Fusion – Combining radar with camera or LiDAR to improve recognition in low-visibility conditions.
- Region-of-Interest Marking – Highlighting radar reflections corresponding to real-world objects.
Applications of LiDAR and Radar

- Autonomous Vehicles – Used together for object detection, obstacle avoidance, and environment mapping; LiDAR provides 3D scene details while Radar measures object distance and speed.
- Robotics & Drones – Enable navigation, collision prevention, and spatial awareness in dynamic or low-visibility environments.
- Smart Cities & Infrastructure – Support 3D mapping, traffic monitoring, and infrastructure inspection.
- Surveillance & Security – Detect and track people, vehicles, or intrusions in all weather and lighting conditions.
- Aviation & Maritime Systems – Assist in terrain mapping, collision avoidance, and target tracking.
- Environmental Monitoring – Used for topographic mapping, forest analysis, flood assessment, and disaster management.
- Agriculture – Support precision farming by analyzing terrain, crop density, and moisture levels.
- Industrial Automation – Enable machine safety, perimeter detection, and intelligent process monitoring.