How Bounding Box Annotation Works
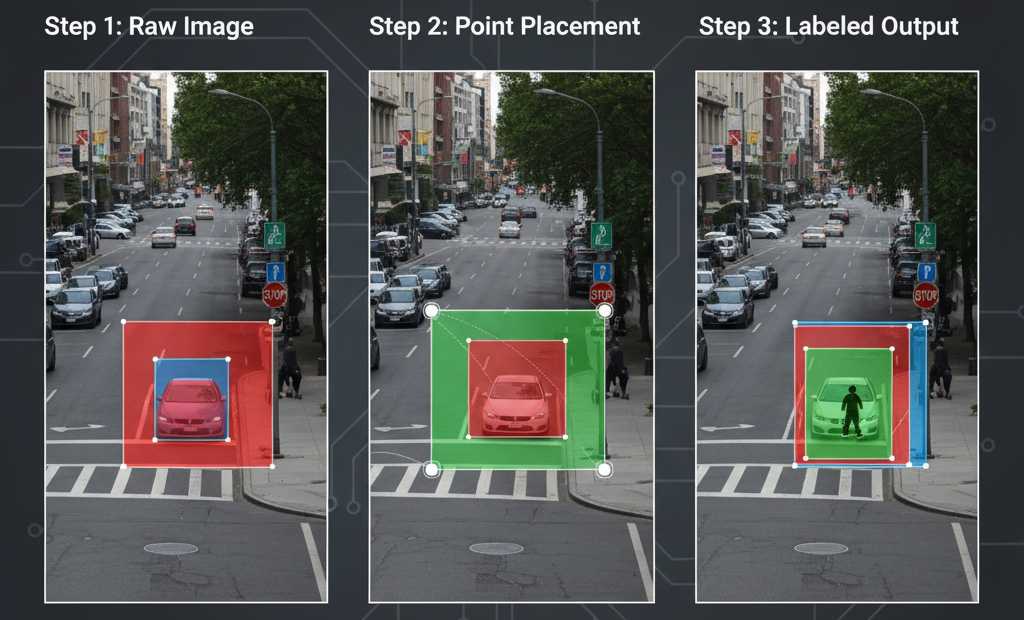
Object Selection: The annotator identifies the object(s) in an image or video frame that need to be labeled.
Box Drawing: A rectangle is drawn around each object, typically using the top-left and bottom-right corners or center coordinates with width and height. The box should cover the entire object while minimizing unnecessary background.
Class Labeling: Each box is assigned a category label (e.g., “car,” “pedestrian,” “dog”) so the model knows what the object represents.
Verification & Refinement: Annotated boxes are reviewed for accuracy, ensuring no objects are missed or mis-labeled.
Dataset Integration: The annotated images are stored in a structured format (like COCO or YOLO), ready for AI model training.
Applications
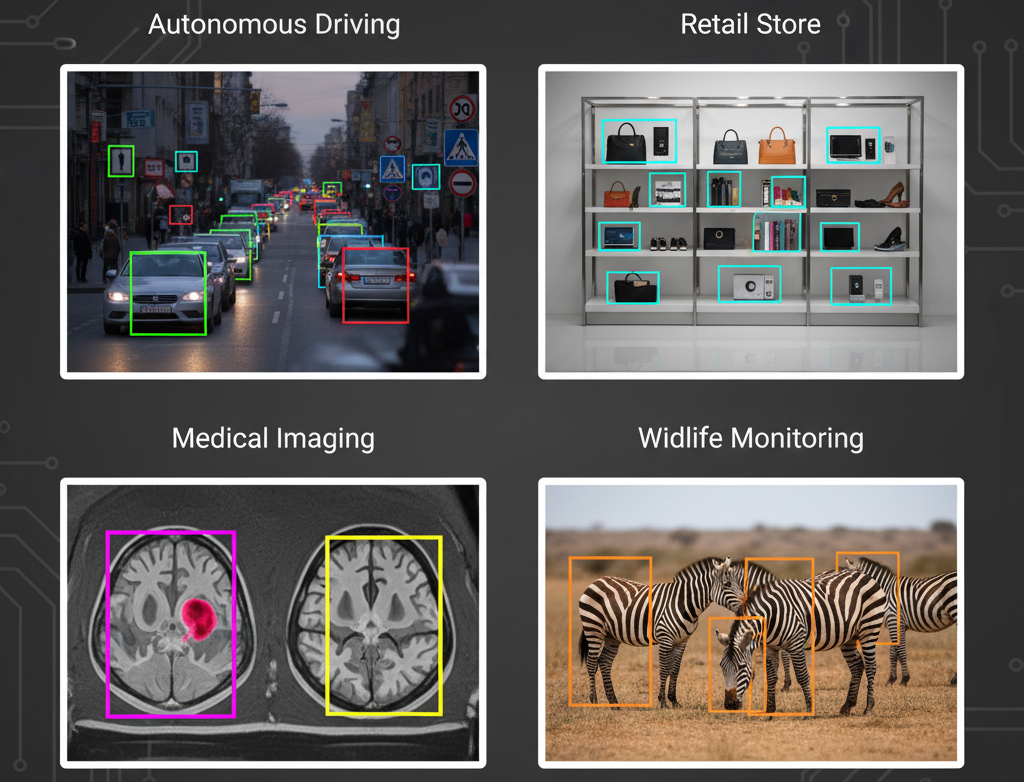
Object Detection: Detecting vehicles, pedestrians, traffic signs, and obstacles in autonomous driving systems.
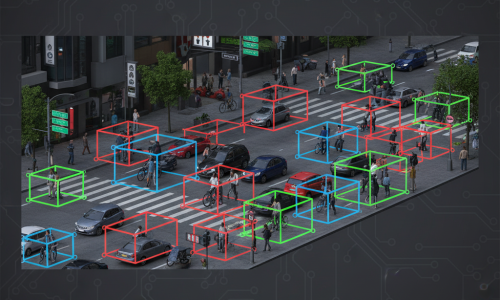
Video Surveillance: Tracking people, vehicles, or moving objects across video frames for security and analytics.
Retail & Inventory Management: Detecting products on shelves or warehouses for stock monitoring and automated checkout systems.
Robotics & Automation: Helping robots locate and interact with objects in real time.
Wildlife Monitoring & Conservation: Tracking animals in images or camera trap videos for research and population studies.
Medical Imaging: Locating lesions, tumors, or organs in X-rays, CT scans, or MRIs as a preliminary detection step.