What is ADAS Annotation?
ADAS (Advanced Driver Assistance Systems) annotation refers to the process of labeling and annotating data (mostly visual) used to train AI models that assist drivers in real-time decision-making. This data is crucial for features like lane-keeping, pedestrian detection, automatic braking, and more.
ADAS annotation involves precisely tagging objects, boundaries, and actions within sensor data—such as video, LiDAR, and radar—to help machines understand road environments accurately.
Why is ADAS Annotation Important?
ADAS features rely on AI to interpret complex driving environments. Accurate annotations are vital to:
- Ensure the safety of autonomous or semi-autonomous vehicles.
- Train models to detect lanes, vehicles, traffic signs, pedestrians, etc.
- Enable decisions like braking, turning, or alerting the driver in real time.
- Reduce false positives/negatives in vehicle perception systems.
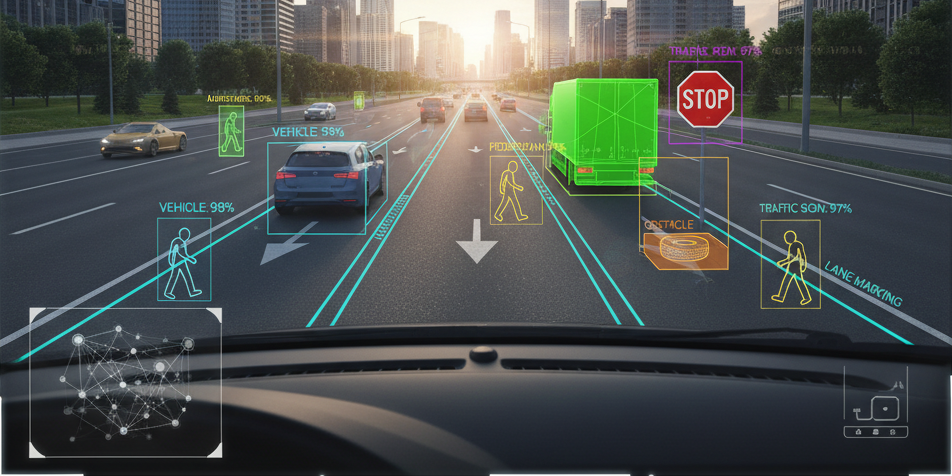
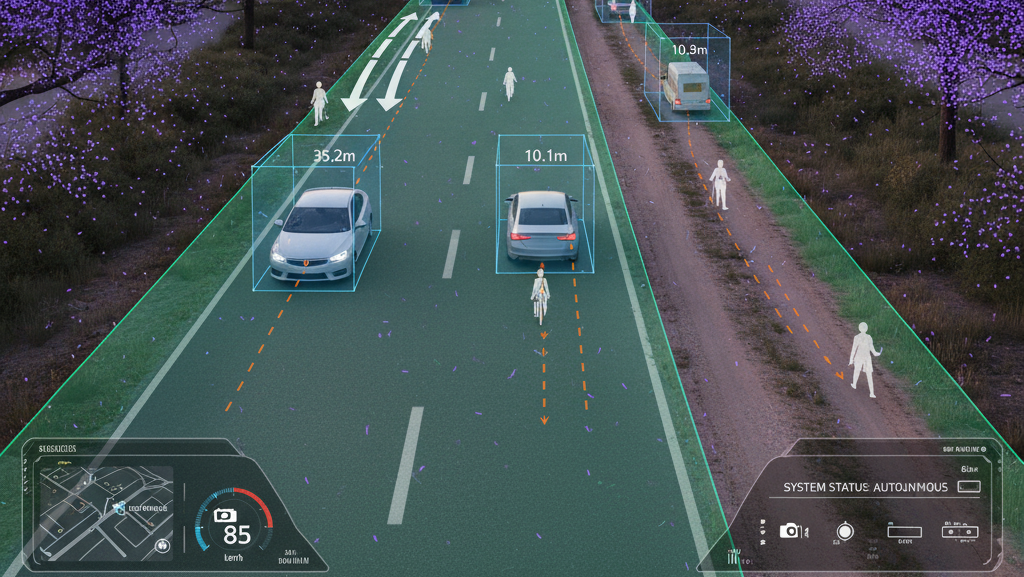
Key Use Cases in ADAS Annotation
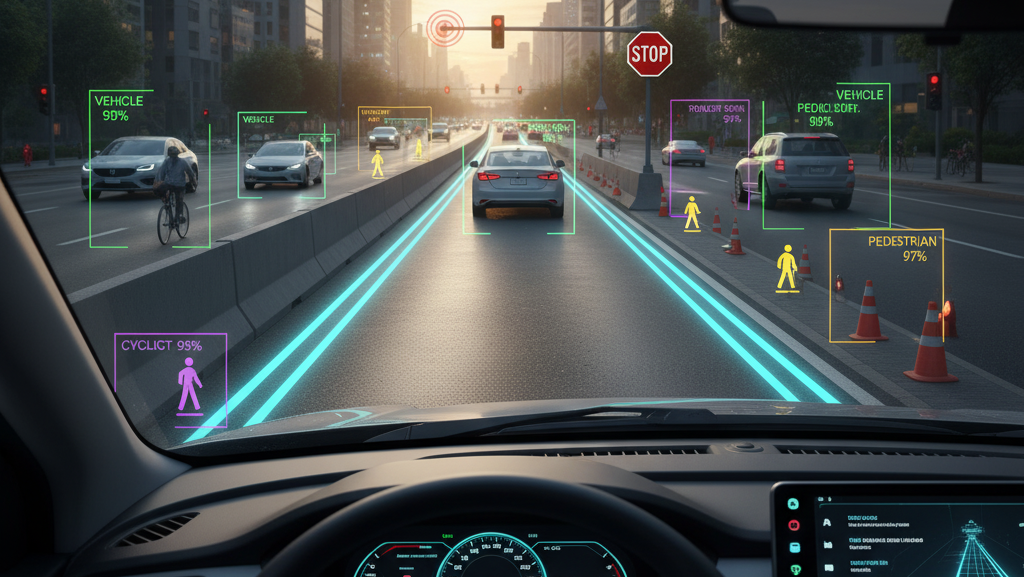

- Lane Detection
Label lane markings and road boundaries for lane departure warning and lane-keeping assistance. - Object Detection and Classification
Annotate other vehicles, pedestrians, cyclists, road barriers, and animals. - Traffic Sign & Signal Recognition
Label and classify signs, traffic lights, and their states (red, green, blinking).
- Drivable Area Detection
Annotate zones where the vehicle can safely navigate, including unstructured roads. - Depth and Distance Estimation
Using LiDAR or stereo images to annotate 3D objects and measure distances. - Behavior Prediction
Annotate the actions or movement trajectories of other vehicles or pedestrians.