What is Natural Language Processing (NLP)?
Natural Language Processing (NLP) is a subfield of artificial intelligence (AI) and linguistics that focuses on the interaction between computers and human (natural) languages. The goal of NLP is to enable machines to read, understand, interpret, and generate human language in a way that is both meaningful and useful.
Key Components of NLP

Text Preprocessing
Tokenization involves breaking text into smaller units such as words or sentences. Stop-word removal eliminates common but insignificant words like “and” or “the.” Stemming and lemmatization reduce words to their root forms, improving text analysis by simplifying variations while retaining essential meaning for better natural language processing.
Syntax and Structure
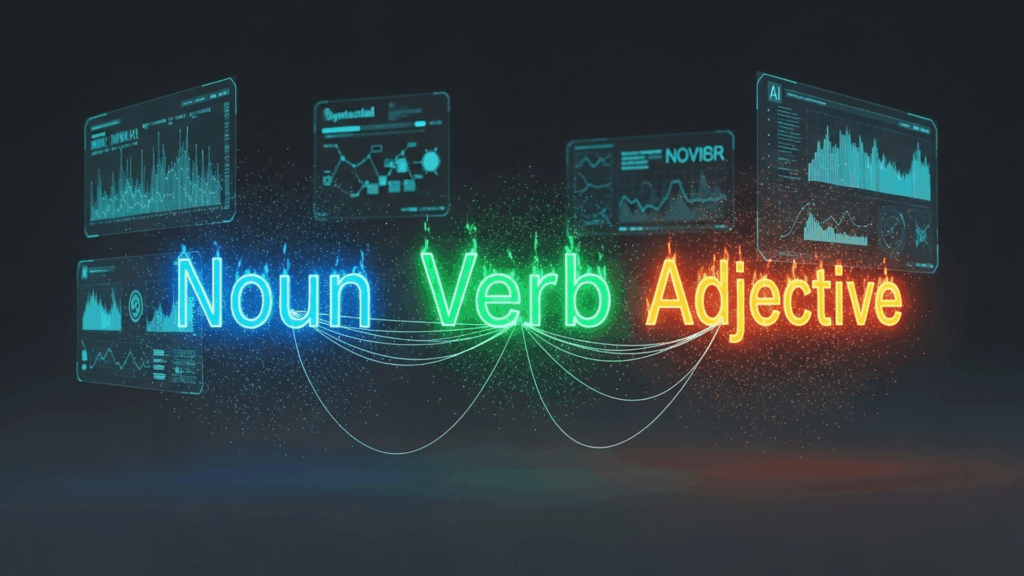
Part-of-Speech (POS) tagging involves identifying each word in a sentence as a noun, verb, adjective, or other grammatical category. Parsing goes further by analyzing the sentence’s structure, applying grammatical rules to understand relationships between words and phrases, enabling deeper linguistic comprehension and more accurate natural language processing.
Semantics and Meaning
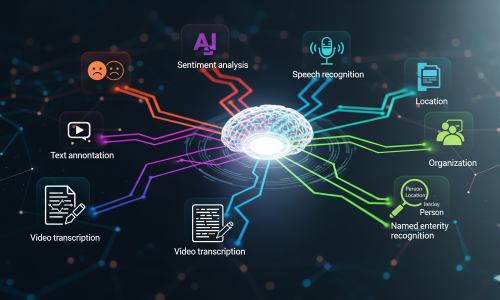
Named Entity Recognition (NER) identifies entities such as names, dates, and locations. Word Sense Disambiguation determines the correct meaning of a word based on context. Sentiment Analysis evaluates text to detect emotions or opinions, categorizing them as positive, negative, or neutral to better understand linguistic nuances.
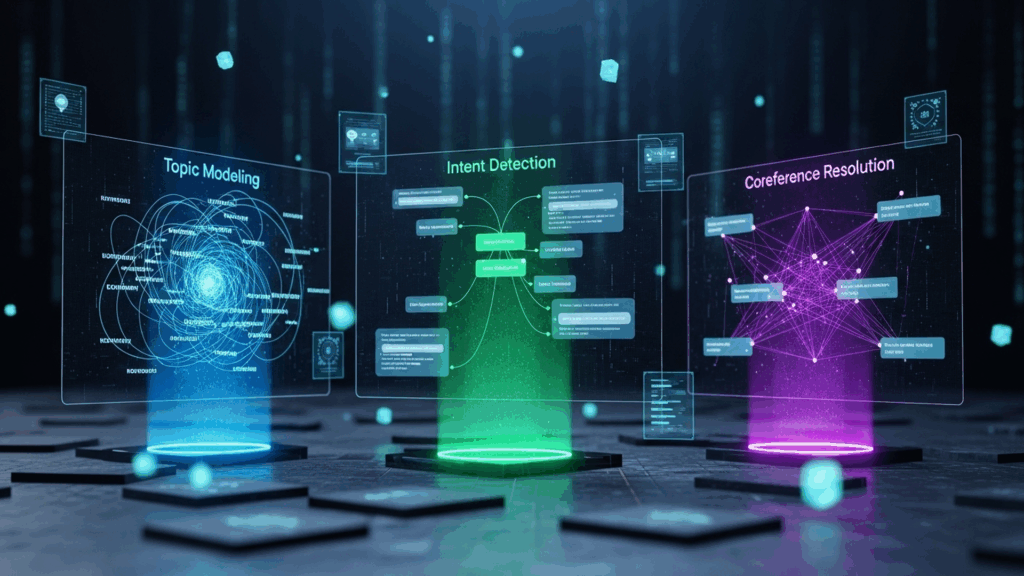
Context and Intent
Topic modeling helps uncover hidden themes within document collections, while intent detection identifies the user’s purpose behind text or queries. Coreference resolution links pronouns and phrases to their correct references, ensuring accurate understanding of meaning and context in natural language processing tasks.