What is Data Annotation and Data Labeling?
Data annotation and data labeling are foundational steps in training machine learning (ML) and artificial intelligence (AI) models. They involve adding meaningful tags, labels, or metadata to raw data—such as images, audio, text, or video—so that machines can learn to recognize patterns, objects, or semantics from the data.
Though often used interchangeably, here’s a nuanced difference:
Data Annotation is a broader term that includes labeling, segmentation, bounding, tagging, and more complex metadata addition.
Data Labeling is the process of assigning one or more labels to raw data samples.
Why is Data Annotation Important?
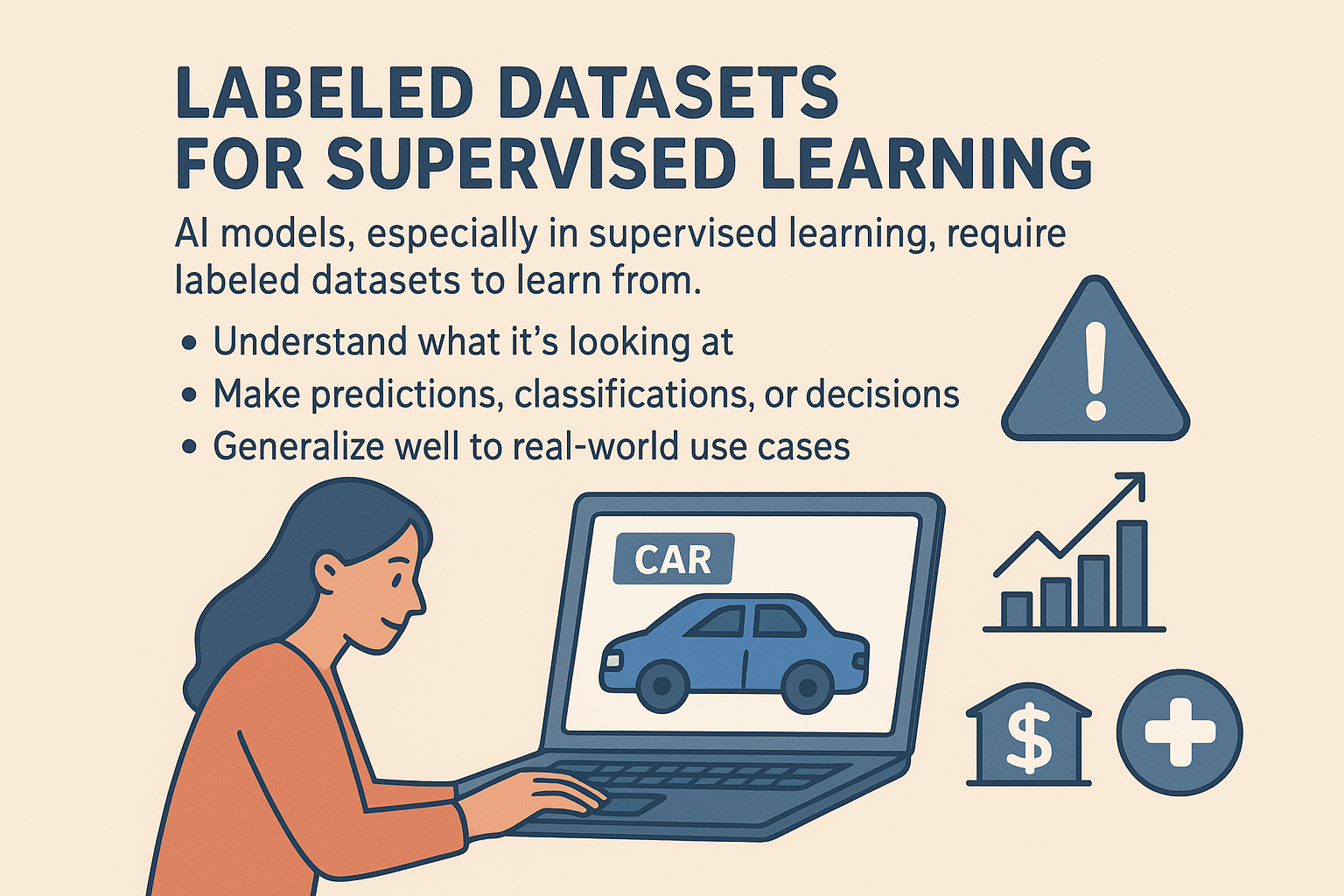
AI models, especially in supervised learning, require labeled datasets to learn from. Without properly annotated data, AI cannot:
- Understand what it’s looking at (e.g., distinguishing between a car and a truck).
- Make predictions, classifications, or decisions.
- Generalize well to real-world use cases.
High-quality data annotation results in better model accuracy, safety, and reliability, especially in critical applications like autonomous vehicles, healthcare diagnostics, and finance.applications like autonomous vehicles, healthcare diagnostics, and finance.
Types of Data Annotation
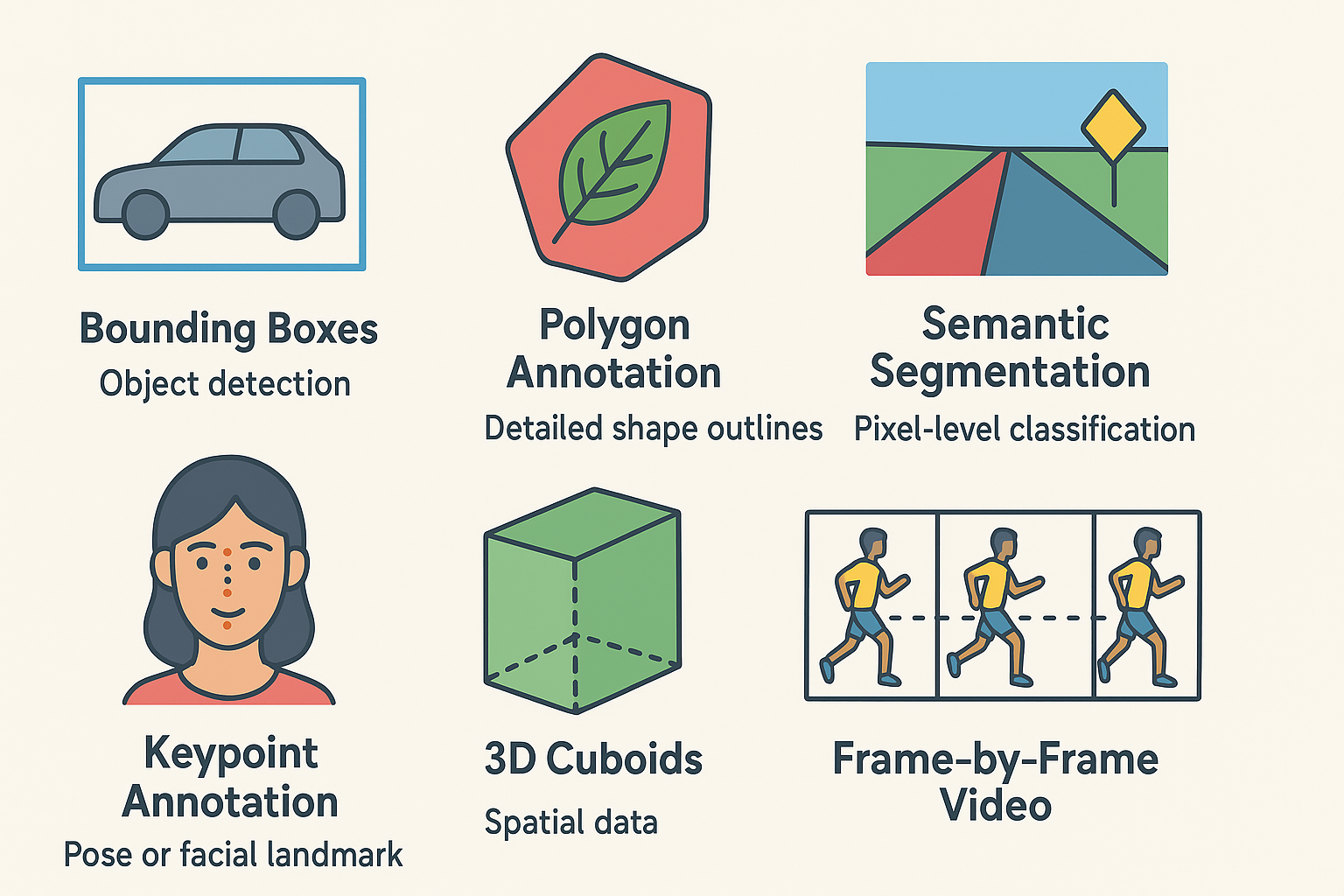
Image and Video Annotation
Image and Video annotation techniques include bounding boxes for detecting objects, polygon annotation for detailed shapes in medical or agricultural AI, and semantic segmentation for pixel-level classification like road mapping in autonomous vehicles. Keypoint annotation marks joints or landmarks for pose or facial recognition, while 3D cuboids capture spatial data in LiDAR. Frame-by-frame video annotation enables object tracking in surveillance and sports analytics.
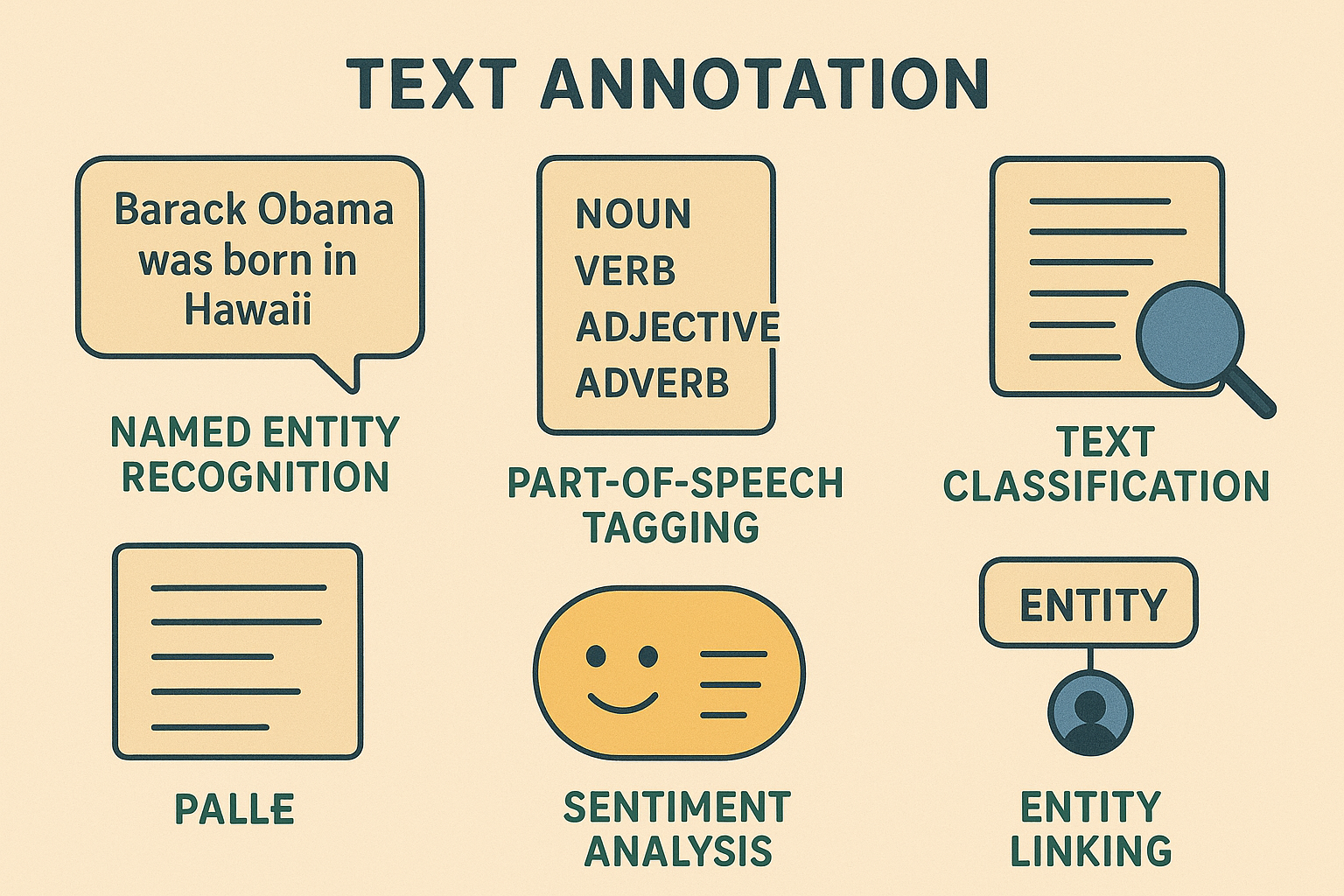
Text Annotation
Natural Language Processing (NLP) techniques power various applications by extracting meaning from text. Named Entity Recognition (NER) identifies names, places, or organizations for use in chatbots and document processing. Part-of-Speech tagging classifies words like nouns or verbs, aiding grammar tools. Intent and sentiment analysis detects emotions in customer feedback, while text classification categorizes documents. Entity linking connects terms to knowledge bases, enhancing search and question answering.
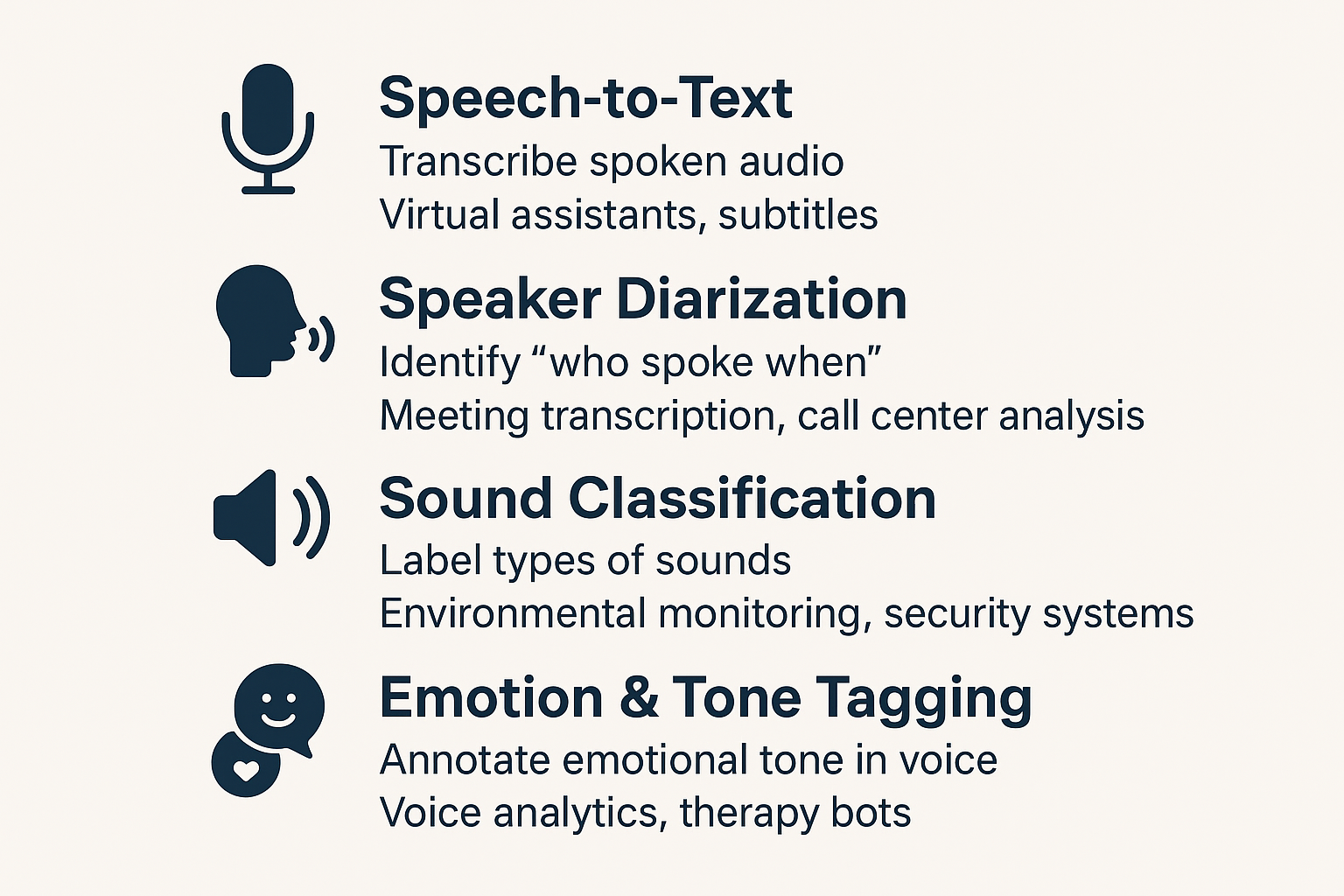
Audio Annotation
Speech-to-text converts spoken audio into written text, useful for virtual assistants and subtitles. Speaker diarization identifies “who spoke when,” aiding meeting transcriptions and call center analysis. Sound classification labels different types of sounds for security and environmental monitoring. Emotion and tone tagging detects vocal emotions, enhancing voice analytics, customer insights, and therapy bots.