What is Interpretation and Structuring?

Interpretation and Structuring refers to the process of understanding unstructured or semi-structured data and organizing it into structured, machine-readable formats so it can be used for analysis, decision-making, or machine learning.
It’s commonly applied to raw text, audio, video, and scanned documents, and is a crucial step in AI pipelines—especially when working with data from real-world sources like emails, reports, conversations, social media, or handwritten notes.
Interpretation: Understanding the Content
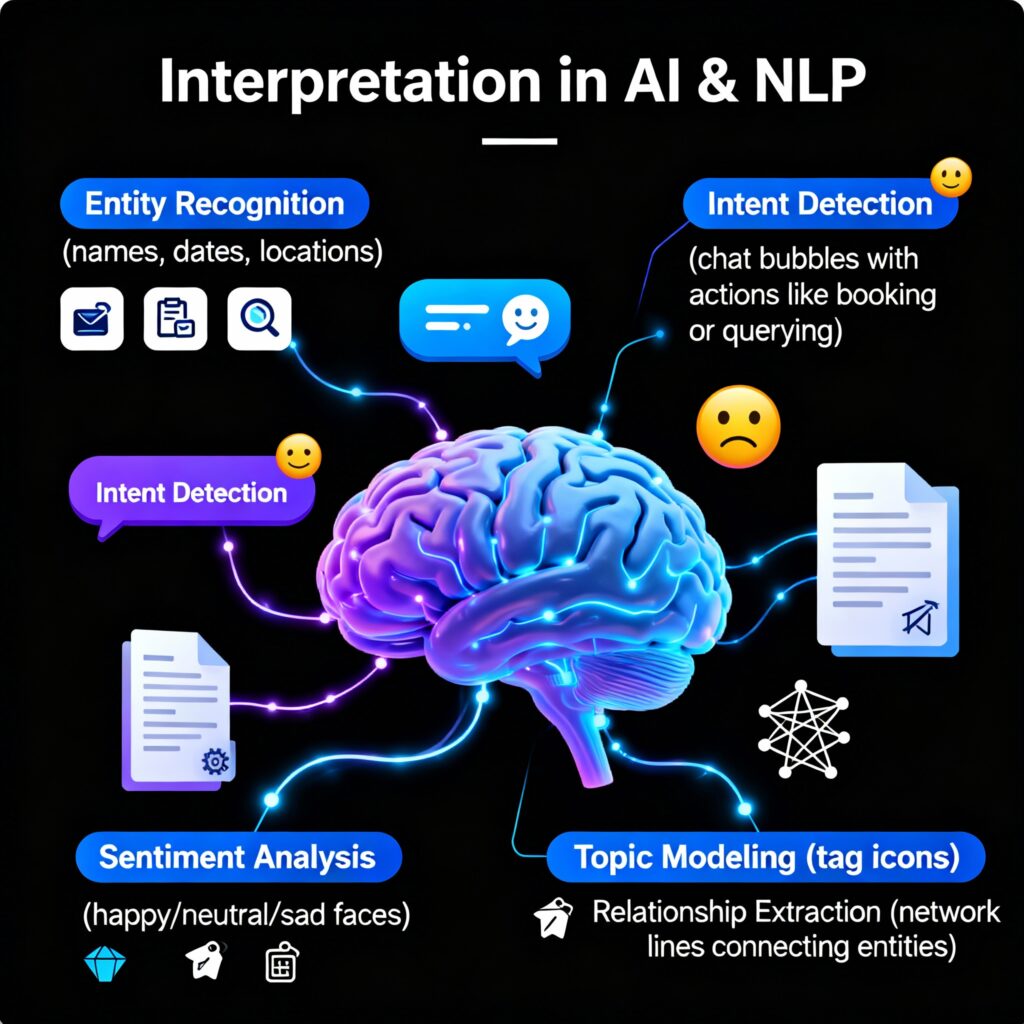
Interpretation in AI focuses on extracting meaning, context, and intent from raw data, enabling machines to understand human input. In NLP and Document AI, it involves tasks like entity recognition (identifying names, dates, locations), intent detection, and sentiment analysis. It also includes topic modeling to classify text, relationship extraction to link entities, and contextual understanding to interpret word meanings accurately based on sentence or document context.

Structuring: Organizing the Data
Once data is interpreted, structuring organizes it into formats usable by AI systems and databases, such as rows, columns, and fields. Common methods include tabular formats (CSV, Excel, SQL) for structured data, and JSON or XML for hierarchical relationships like form fields. Knowledge graphs connect entities through semantic links, while labeled training data transforms text into annotated tokens, supporting tasks like Named Entity Recognition (NER) and other NLP applications.

