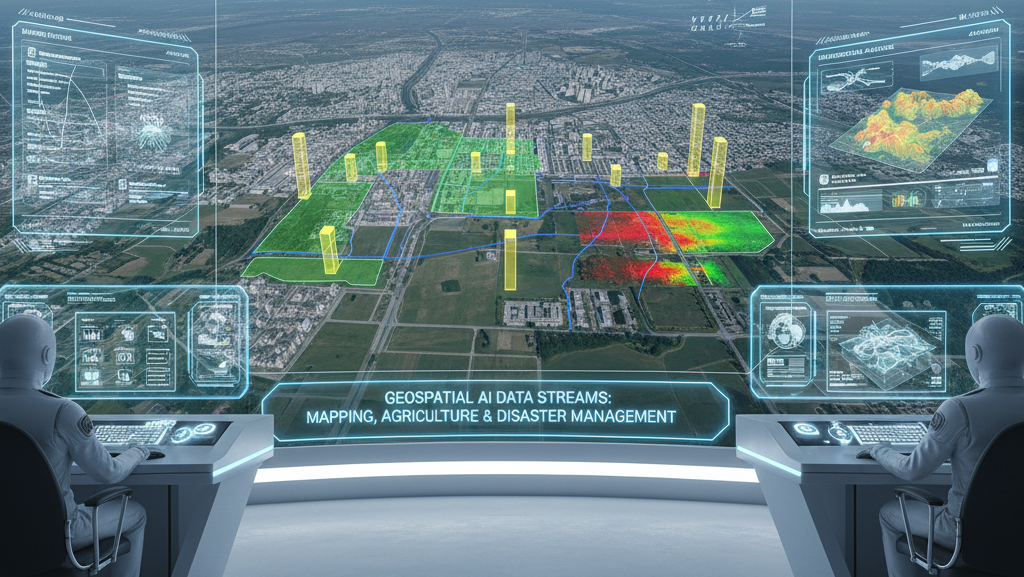
Why Annotation is Important in the Geospatial Industry

- Feature Identification: Annotated satellite and aerial imagery allows AI to distinguish between roads, rivers, forests, and urban areas.
- Change Detection: By comparing annotated geospatial data over time, AI can detect deforestation, urban growth, flooding, or other environmental changes.
- Disaster Management: Accurate annotations help AI models quickly identify affected zones, damaged infrastructure, or safe evacuation routes.
- Precision Agriculture: Annotating farmland, irrigation systems, and crop health indices enables AI-driven optimization of resources.
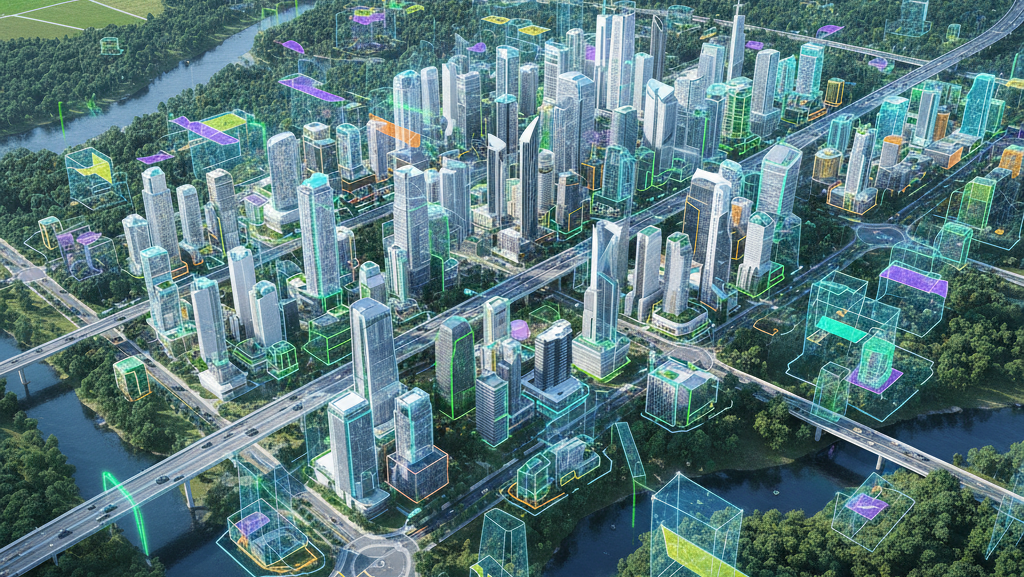
- Urban Planning & Smart Cities: Annotation helps map buildings, utilities, and infrastructure for informed city planning and resource allocation.
Types of Geospatial Annotation
- Image and Aerial Annotation: Annotating satellite or drone images with polygons, bounding boxes, and semantic segmentation to classify land types, buildings, roads, water bodies, and vegetation.
- 3D Annotation (LiDAR/RADAR): Annotating point clouds and 3D data to understand terrain elevation, building heights, vegetation density, and infrastructure layouts.
- Polyline & Keypoint Annotation: Mapping linear features such as roads, rivers, pipelines, and railways, and marking keypoints like bridges, towers, or landmarks.
- Multispectral and Hyperspectral Data Annotation: Labeling different spectral bands to assess vegetation health, soil moisture, mineral deposits, or water quality for environmental and agricultural applications.
- Change Detection Annotation: Annotating temporal geospatial datasets to train AI models for detecting urban expansion, deforestation, or disaster impact over time.