How Keypoint Annotation Works
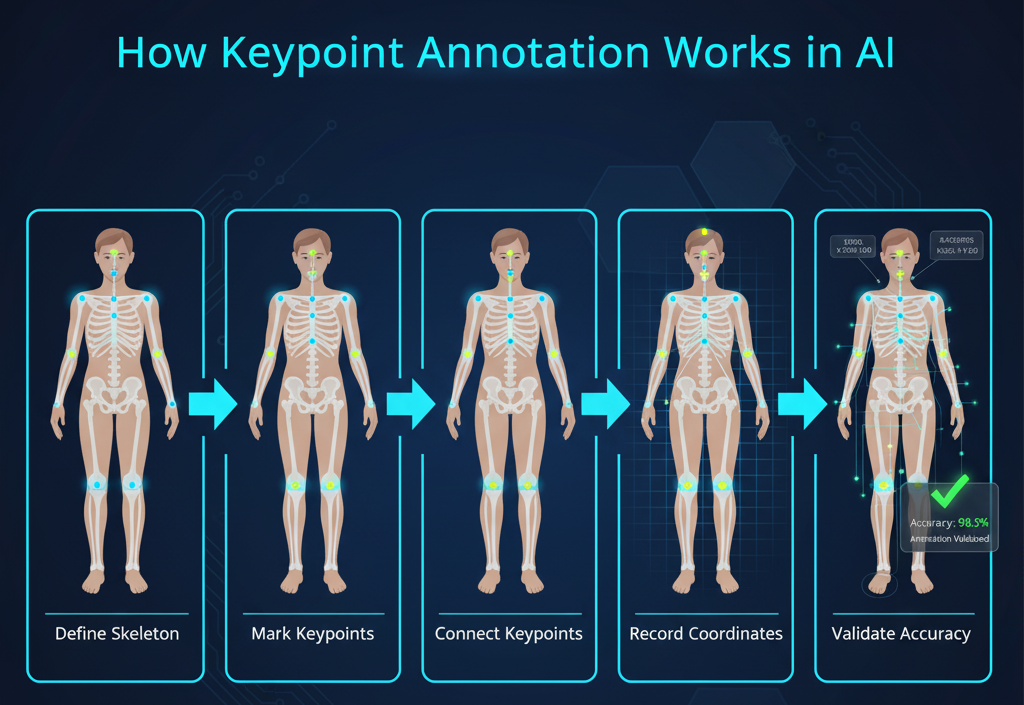
Defining the Schema: Before annotation begins, a predefined structure or “skeleton” is created — specifying which keypoints (e.g., nose, elbows, knees) should be marked.
Manual or Semi-Automated Marking: Annotators manually place points on the defined positions, or AI-assisted tools suggest positions for human validation.
Coordinate Recording: Each keypoint’s X and Y coordinates (and sometimes Z for 3D data) are stored in datasets.
Connecting Relationships: Keypoints are linked with lines to form skeletons or outlines, showing spatial relationships and movement paths.
Quality Validation: Annotated data undergoes quality checks to ensure accuracy and consistency across images.
Augmentation & Model Training: The annotated images are then used to train AI models that detect or track these points automatically in new data.
Types of Keypoint Annotation
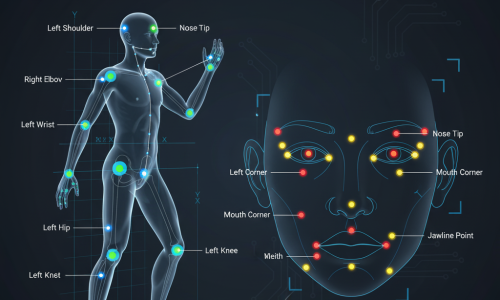
Human Pose Estimation: Keypoints mark body joints (e.g., wrists, shoulders, knees) to study motion or gestures.
Facial Landmark Annotation: Labels facial points such as eyes, eyebrows, nose, mouth, and jawline for emotion or identity recognition.
Object Keypoint Annotation: Identifies critical parts of machinery, vehicles, or tools (e.g., wheel centers, handles, or corners).
Animal Keypoint Annotation: Marks body parts (legs, tail, ears, snout) for behavior tracking and veterinary research.
Hand Pose Annotation: Focuses on finger joints and palm centers for gesture recognition and AR/VR applications.
Foot & Gait Analysis: Used in sports or healthcare to study walking patterns by marking ankle and foot joints.
Medical Keypoints: Marks anatomical landmarks (e.g., bone joints, organs) in medical imaging for diagnostic AI.
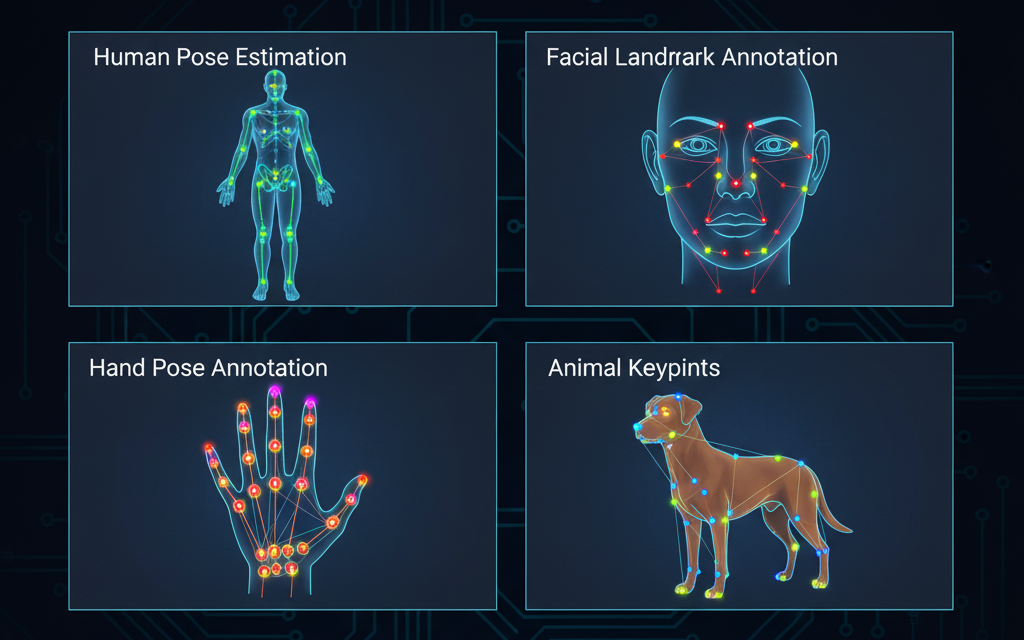
Applications

Human Activity Recognition – Used in sports analytics, healthcare, and gesture control.
Facial Recognition & Emotion Detection – Mapping facial landmarks to identify expressions or individuals.
Autonomous Vehicles & Robotics – Detecting pedestrians and analyzing human poses for safe navigation.
AR/VR and Animation – Capturing motion and facial expressions for avatars or characters.
Industrial Inspection – Monitoring equipment posture or mechanical part alignment.